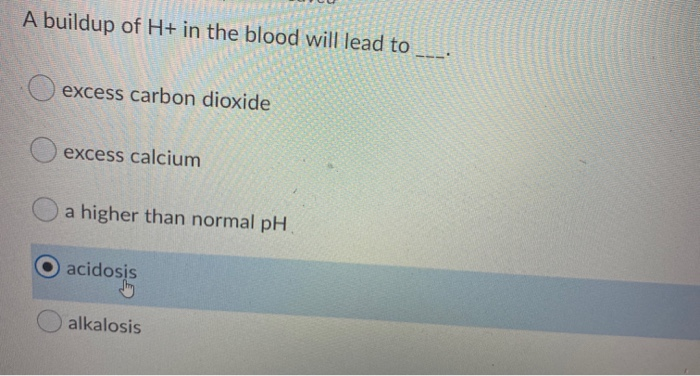
A Buildup of H+ in the Blood Will Lead to
This is because an enzyme called carbonic anhydrase rapidly converts CO2 and water into a substance called carbonic acid H2CO3 which in turn can rapidly turn into HCO3-. This is called respiratory acidosis.
Any condition that decreases movement of CO 2 out emphysema pulmonary edema airway obstruction can lead to this Kidneys can help raise blood pH by increasing excretion of H and reabsorption of HCO 3.

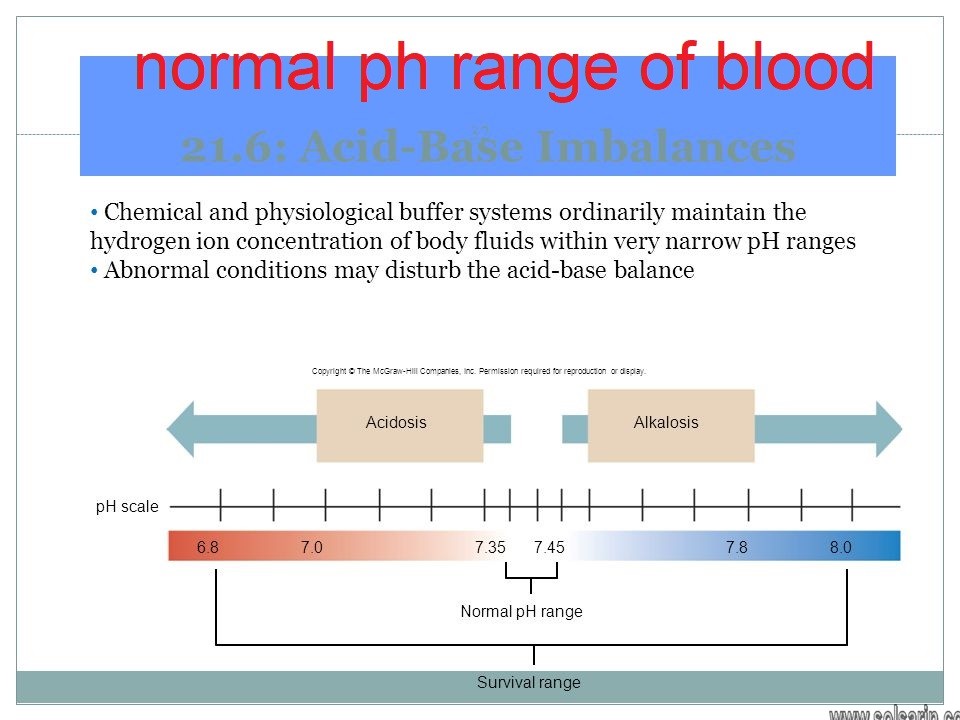
. High blood pH above 745 is called alkalosis. Finally there are certain substances that can lead to metabolic acidosis by promoting anaerobic metabolism and in turn lactic acid production. Carbonic acid will then dissociates into carbon dioxide CO2 and water.
Wions pH acidic environ Renal Failure End-Stage. As a result the concentration of H ions in the bloodstream rises lowering the pH and causing an acidosis-like state. As a result the concentration of H ions in the bloodstream rises lowering the pH and causing an acidosis-like state.
Acidosis - acid buildup H in blood leads to increased RATE and DEPTH lactic acid Exercise and Altitude Effects. In the blood it passes from the cells to the heart. This is often the case during the last days or hours of life in people who are chronically and terminally ill.
In contrast when CO2 levels are low there is a left shift in the reaction resulting in an alkalotic state. Carbonic anhydrase catalyzes the conversion of CO2 and water to H and bicarbonate. All three of those conditions indicate poor perfusion or oxygen delivery to tissues which can occur for a myriad of reasons.
While these are generally short-term effects of toxin buildup long-term effects can lead to harmful even life-threatening consequences. Ultimately decrease in CO2 leads to increase in blood pH and if not stopped our brain will shut down the body. 2Nephron tubular fluid is more alkaline due to decreased reclamation of filtered bicarb.
Blood volume - by filtering blood excreting or reabsorbing water from body as needed influenced by hormones ADH ANP Aldosterone 2. Severe alkalosis when blood pH is more than 8 can also lead to death. Blood pH by controlling reabsorptionexcretion of H HCO 3.
1 respiratory depression 2 leads to hypermagnesemia 3 results in metabolic acidosis H build up dt malfunctioning kidney not passing off excess H ions. PH Effects H ion. Acid-Base Balance in the blood is regulated SEQUENTIALLY by.
An increase in H or a fall in pH is termed acidemia which is caused by acidosis. Blood pressure by regulating blood volume. The buildup of the products of nucleic acid metabolism can lead to.
An increase in H count lead to alteration in acid-base balance. When blood volume and pressure are low the juxtaglomerular apparatus secretes renin. H H2CO3 HCO3- and H Thus the overall pattern is.
3 1 chemical buffers - react instantly 1st line of defense. Historically Hhas been thought to have a role in the development of muscle fatigue. Salicylates overdose can also lead to high gap metabolic acidosis in the later phases due to the buildup of H in the blood.
This is a defence mechanism hense a significant variation in pH may lead to death. Glycolysis leads to the production of pyruvate which feeds into the TCA cycle for oxidation. H2O CO2 H2CO3 HCO3- H Therefore if breathing is restricted CO2 builds up and the reaction shifts to the right in an attempt to balance things out ultimately making the blood more acidic and thus decreasing its pH.
If pyruvate production exceeds its oxidation excess pyruvate is converted into lactic acid which dissociates into lactate and H. When blood pressure is high the heart atria secrete ANH. Blood osmolarity by controlling reabsorptionexcretion of salts Na Cl- K Ca2.
In metabolic acidosis blood HCO3- concentration decreases which increases H concentration. As a result the concentration of H ions in the bloodstream rises lowering the pH and introducing a state of acidosis. This process is made possible with the assistance of carbonic anhydrase enzyme produced on RBCs.
A high concentration of H will decrease PCr by a direct effect on the creatine kinase equilibrium and indirectly by an increase in ADP. Regulation of pH of body fluids. 3 fatty acids and ketone bodies.
Naturally CO2 will begin to build up in the blood hypercapnea tissues will be low in oxygen hypoxia and the pH will become relatively acidic because of the decreased HCO3-CO2 ratio in the blood. 2 brain stem respiratory centers - react wn 1-3 minutes changing respiratory rate. The effect of acidosis on glycolysis and on the PCr level will result in a decreased rate of ADP rephosphorylation and it is suggested that ADP increases transiently above the steady-state level in the contracting muscle fibre.
Any condition that causes a buildup of CO 2 in the blood could eventually lead to hypercapnia. Hyperventilation is the most common cause of respiratory alkalosis. H combines with bicarbonate ions resulting in the formation of carbonic acid.
In healthy people blood pH is maintained around 74. 1Metabolic acidosis - bone releases Ca and PO4 to buffer the acid - this increases the amount of Ca and PO4 in the urine. A higher than normal pH.
How Are Blood Ph And Co2 Related. High H levels can eventually disturb body metabolism. Some signs that your body has a toxin buildup include.
Buildup of F1P leads to low blood glucose glucose is soaked up by the cell instead of staying in the blood because F1P has lead to glucokinase to remain in the cytoplasm and not sufficient energy existing and ultimately can cause damage to the liver. A buildup of H in the blood will lead to ____. F1P would build up and phosphate which attaches to fructose would decline.
NH3 H NH4 the need to reabsorb more water. A left-shift reaction occurs when CO2 levels are low resulting in an alkalotic state. Exercise Effects hyperpnea -.
The above two together lead to Ca phosphate stones.

Deprotonation Of Alpha C Mcat Alpha Electrons
Normal Ph Range Of Blood Perfect Description
Solved A Buildup Of H In The Blood Will Lead To Excess Chegg Com
No comments for "A Buildup of H+ in the Blood Will Lead to"
Post a Comment